Sysinternals tools are a go-to resource for every IT administrator and cybersecurity professional I’ve met, but chances are you might have never used them yourself. These tools don’t come pre-installed on Windows and are typically used by advanced users like developers, but they’re just as valuable for everyday users.
The Sysinternals suite includes a wide range of powerful utilities that provide detailed system information you normally wouldn’t have access to, along with deep control over the Windows environment. They help you monitor, diagnose, troubleshoot, and better understand Windows systems and applications, offering insights and capabilities far beyond built-in tools like Task Manager or Event Viewer.
Related
5 built-in tools to use when troubleshooting Windows problems
You don’t need third-party tools
6
AutoRuns
Use it to clean up unnecessary startup programs
Autoruns is a startup management tool that shows you every program configured to run automatically on your PC. It reveals not just the apps and drivers set to launch at boot or user logon, but also hidden entries tucked away in Startup folders, the Registry (Run, RunOnce, services, Winlogon, and more), shell extensions, scheduled tasks, and beyond. In short, it goes far beyond what the standard Task Manager can see.
You can use Autoruns to remove unnecessary startup programs, speed up boot times, and free up system resources. For example, if your PC is slow to boot, Autoruns might uncover a hidden updater or driver that loads during login and can be safely disabled. It is also an essential tool for troubleshooting, as it shows you exactly where an unexpected program is registered if it keeps launching.
5
RamMap
Diagnose memory issues
RamMap is an advanced physical memory analysis tool that helps diagnose memory issues and optimize performance. If your system feels sluggish or runs out of RAM, you can use RamMap to determine whether cache, drivers, or a specific process is consuming the majority of the memory. You can also compare snapshots taken before and after launching a heavy application to see its impact.
RamMap answers questions like how much RAM Windows is using for file cache compared to applications, and which files have their data cached in memory. The tool breaks down RAM usage across several tabs. For example, “Use Counts” summarizes memory by type, such as standby or modified, “Processes” shows each process’s working set, “Priority Summary” displays standby list priorities, and “File Summary” and “File Details” list which files have data occupying RAM. You can refresh the view in real time or save memory snapshots to analyze later.
4
DiskView
See a graphical map of your disk’s clusters
DiskView provides a graphical map of your disk’s clusters. You can use it to visually locate large hidden files by identifying large, colored regions on the map. If you suspect a file is leaking or leftover files remain, DiskView shows whether those clusters are free or still in use. It can also reveal fragmentation because a heavily fragmented file will appear as many scattered blocks.
DiskView paints the hard drive layout by coloring each block to show whether it is free or used, and if used, which file occupies it. By clicking or double-clicking a block, you can identify the exact file that resides in that cluster. This lets you locate files and visualize disk usage at a very low level.
3
Process Explorer
See what’s running on your system
Process Explorer is a must-have for troubleshooting your system. If your disk or CPU is bogged down, it helps you quickly identify which process is causing the issue. If you can’t delete a file because it’s in use, just search for the process that’s locking it. It’s also awesome for debugging, especially when you’re tracking down handle leaks or mismatched DLL versions.
Its key features include a detailed process tree that shows all your processes and threads, plus real-time graphs for CPU, GPU, I/O, and memory usage. You can see which files or DLLs a process has open. The search tool lets you find processes by handle or DLL name, so you can easily spot the one using a specific file. You can also kill, suspend, change the priority, or check out the properties of any process. Hovering over a process gives you tooltips with info like version, company, and more.
2
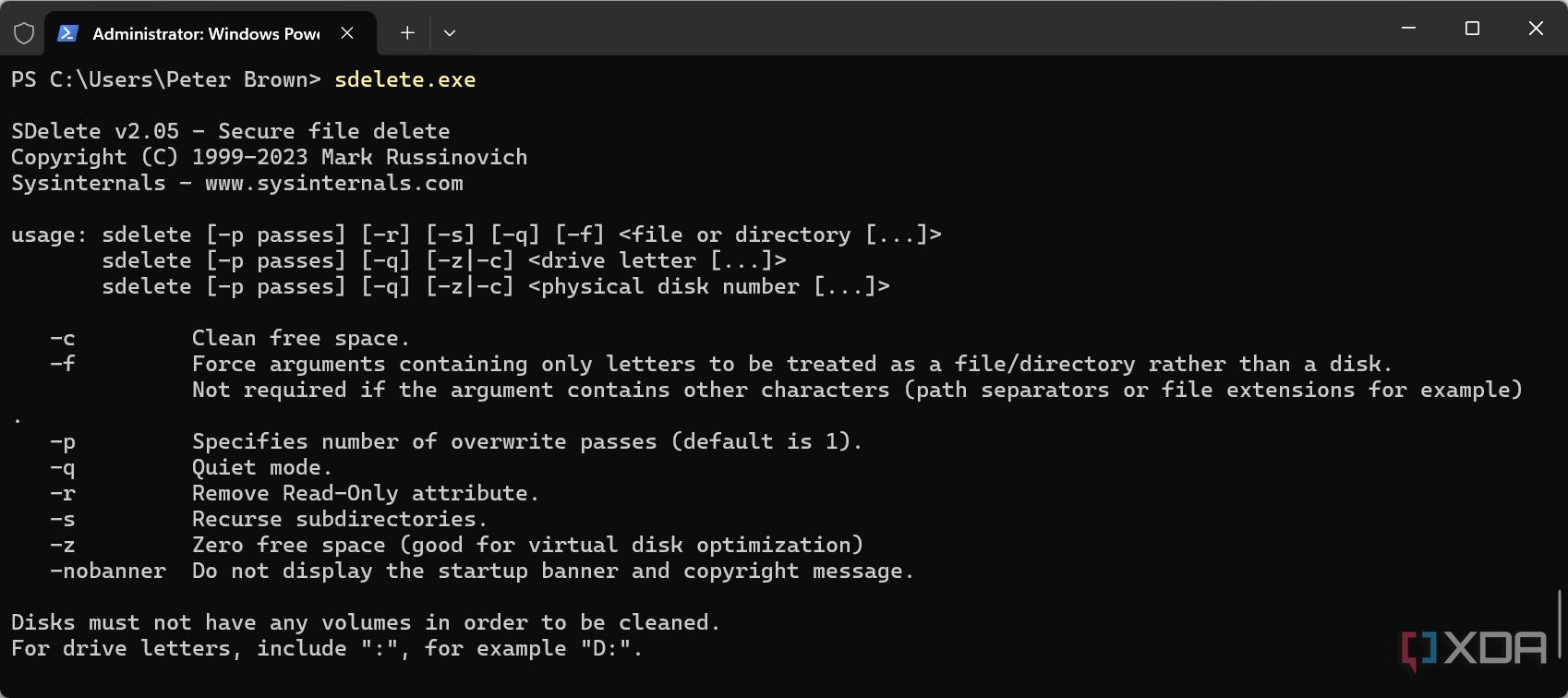
SDelete
Permanently erase files
SDelete (Secure Delete) is a command-line tool for permanently erasing files. Normally, when you delete a file, its data stays on the disk until it’s overwritten, making it possible to recover. SDelete fixes this by overwriting the file’s data (and even free space) with secure patterns, following the U.S. DoD 5220.22-M standard. This makes the file’s data pretty much unrecoverable once it’s deleted. You can use SDelete to wipe specific files or clean up the free space on entire drives.
SDelete is great for protecting your privacy and data security. For instance, before giving away or imaging a hard drive, you can use SDelete to scrub all deleted files and wipe traces of old documents. Running sdelete -z C: zeroes out free space, hiding old data and even shrinking virtual disk images.
1
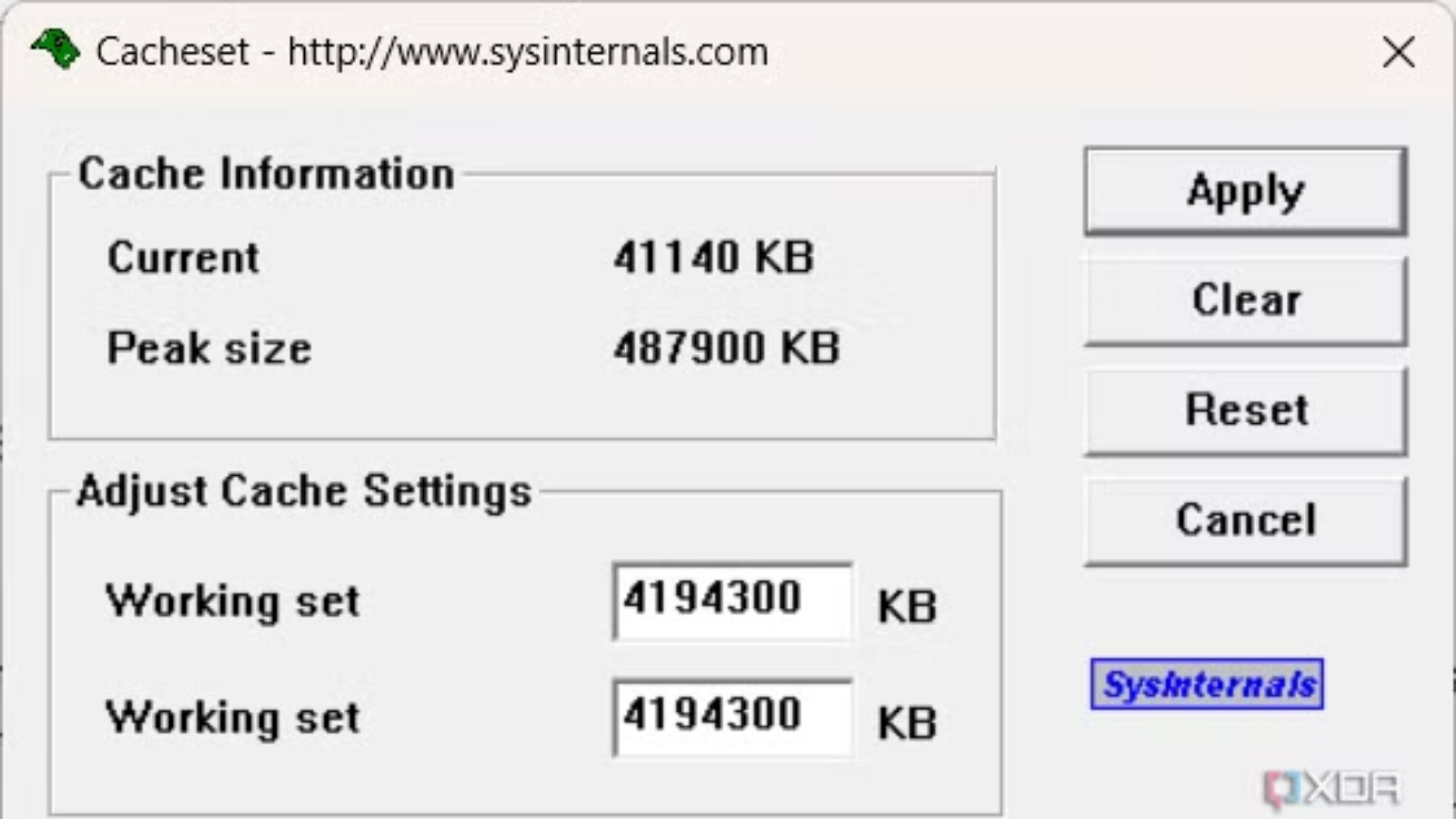
CacheSet
Tweak Windows’ system file cache
CacheSet is a simple tool for tweaking Windows’ system file cache. Windows uses some of your RAM to cache disk files, but there are times when an app might need more memory or you might want to limit the cache size. CacheSet lets you adjust the minimum and maximum working set size of the file cache. You can shrink the cache or reset it to a smaller size, and the change takes effect right away—no reboot required. Plus, it has a live display showing the current and peak cache size, so you can see how it changes as apps run.
CacheSet is especially helpful for performance tuning. For example, on a server doing a lot of file operations, you might allocate more RAM to the cache to speed up disk reads. On the other hand, if you’re running memory-hungry apps on a workstation, you can limit the cache to free up more RAM for those apps.
Make the most out of SysInternals tools
SysInternals tools can make troubleshooting Windows a lot easier. If you’re just starting out, it’s worth checking out some of the best SysInternals tools for power users. You might also want to explore tools that can help optimize your Windows device. If you’re after other ways to troubleshoot, you can check out these PowerShell commands or these Command Prompt commands.

Related
5 reasons Sysinternals tools are essential for diagnosing advanced Windows issues
It gives you ultimate control over your Windows PC